Decimal system
The decimal numbering system is also known as a decimal system and consists of a positional numbering system. This positional system is a set of symbols and rules that allow us to form all the numbers that exist and that are valid. In the decimal system, quantities can be represented using arithmetic bases, ten powers. The Arabic or Indo-Arabic numbers are the symbols used to represent the decimal system and it is composed of ten different digits: zero (0), one (1), two (2), three (3), four (4), five (5), six (6), seven (7), eight (8), nine (9). This system is used worldwide and in all mathematical aspects.
What is the decimal system?
The decimal system is a numbering system composed of a series of symbols that, respecting different rules, are used to build the different valid numbers taking into account the ten base. It is the way to represent quantities using ten digits from 0 to 9.
What is the decimal system for?
The decimal system is a necessary system in our daily lives. Most of the things we do are surrounded by numbers and it is necessary to have a way of expressing them in order to perform different activities, measure an object, perform different calculations, pay the bill in a store or restaurant. The decimal system allows us to construct all the numbers that are valid in the system. It is a way of counting numbers. This system is a way that humanity has accepted to count. Another important function of this system is that it helps us to communicate, because it helps us to represent things and large quantities, since numbers that are too large could not be easily represented.
Characteristics
- It is a decimal system because ten units of a given order correspond to one unit of the higher order.
- The decimal numbering system uses the number 10 as a basis.
- Because it is a positional system, the value of each number or digit will depend on its position within the numeric figure.
- The sum of all the digits of the number multiplied by each power will give us the value of this number.
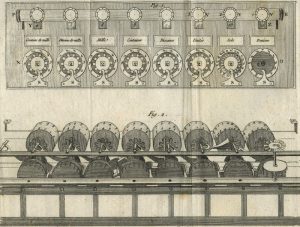
History
From very ancient times, civilizations used different types of numbering systems to represent numbers. Some of them, like the Roman or the sexagesimal systems that were used in ancient Babylon, can still be observed today in our society, being the case, for example, when we use Roman numerals to represent centuries or years, or time, when we write it as 18:56. According to studies conducted by different anthropologists, the origin of this system is in hand fingers, which have been used for centuries to count. The development of numbers 1 to 9 originated in India, according to what was rescued from the Inscriptions of Nana Ghat, which date from the 3rd century BC. Sometime later, the Arabs began to use the numbers we know today.
Who invented the decimal system
This numerical system was created by Hindu peoples. Sometime after this system was created in India, the astronomer, mathematician and geographer Al-Khwarizmi, who was born in Persia in the year 780, introduced the decimal numbering system that is currently used all over the world. Al-Khwarizmi studied for a long time this system and the correct way to use it to make calculations with it. He perfected it with his own contributions and looked for a way to be able to use zero as a number. Thanks to his work, the system was translated into Latin and managed to be included in Europe, where it was decided to abandon the Roman numbering system and adopt the decimal numbering system. Today, the system is used all over the world and, because it came to Europe through the Arabs and the works of Al-Khwarizmi, it is also known as the Arabic numbering system.
Decimal system symbols
The symbols used by decimal system are the numbers from 0 to 9, and each of these numbers is associated with a certain value that depends on its position, the further to the left the number is, its number will be ten times more than it is worth. As such, in a natural number we can find the following figures:
- Units, the value it represents is worth,
- Tens, it’s worth 10 times its value,
- Hundreds, it’s worth 100 times its value,
- Thousand units, worth 1000 times its value,
- Tens of thousands, it’s worth 10000 times its value,
- Hundreds of thousands, worth 100,000 times its value,
- Units of a million, worth 1000000 times its value,
- Tens of a million, it’s worth 10,000,000 times its value,
- Hundreds of a million, it’s worth 100,000,000 times its value,
Examples
- 539: In this number, the 3 occupies the place of the tens, therefore, its value is 30 (3 x 10). In order to understand it better the number can be broken down: 500 + 30 + 7
- 329: In this number, the 3 occupies the place of the hundreds, therefore, its value is 300 (3 x 100). So, the decomposed number will be: 300 + 20 + 9
How to cite this article?
Briceño V., Gabriela. (2019). Decimal system. Recovered on 24 February, 2024, de Euston96: https://www.euston96.com/en/decimal-system/