Gestalt theory
Gestalt theory or psychology is a school of thought that observes the human mind and the behavior of the human being as a whole. When trying to make sense of the world around us, Gestalt psychology suggests that we should not simply focus on every small component. Instead, our minds tend to perceive objects as part of a larger whole and as elements of more complex systems. This school of psychology played an important role in the modern development of the study of human sensation and perception.
What is the Gestalt theory?
It is a current of modern philosophy which emerged in Germany and which is based on the assertion that the whole is always more than the sum of its parts.
About Gestalt theory
The holistic thought on which the theory is based can be summed up in the statement that the whole is always more than the sum of its parts. This sentence explains to us that all the principles of the theory of this current seek to discover the reasons why the human brain tends to interpret a set of different elements as a single message, and the way in which the mind is able to group the information we receive into different mental categories that have been established by ourselves. According to Gestalt theory, the core is the whole and the different individual elements that compose it have no importance or meaning of their own. The school maintains that it is the mind that is in charge of configuring the elements that enter through the perception of memory.
History
The theory is born as a reaction to values that were already established and based on psychoanalysis and behaviorism. It was born in the 1940s through the publication of the book “Ego, Hunger and Aggression: A revision of Freud’s theory and method” which was written by Fritz Perls and Laura Perls, for this reason, it is considered that its creator was Fritz Perls, a Jewish psychiatrist, although there were several people who influenced the theory. In the beginning, the therapy had a name and was not intended to become a school. In 1951, in New York, the theory began to be known. In this year Gestalt Therapy is published, under the authorship of Fritz, Perls, Ralf Hefferline and Paul Goodman, in which the theoretical guidelines and theoretical bases were established.
Principles of Gestalt theory
The Gestalt theory is based on the following principles:
- The pregnancy principle: use the perceptive experience to adopt the simplest forms possible.
- Principle of similarity: our mind gathers similar elements in a single entity.
- Principle of proximity: the elements are grouped when the parts of a whole receive the same stimulus.
- Principle of symmetry: symmetrical images are perceived as equal.
- Principle of continuity: details that have a pattern or direction are grouped together as part of a model.
- Principle of simplicity: the individual organizes his perceptual fields with simple and regular features.
- Principle of common direction: elements that construct a pattern in the same direction are perceived as a figure.
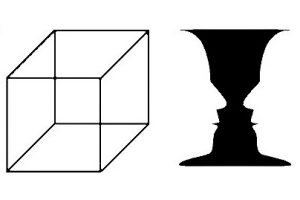
- Principle of relationship between figure and background: the brain cannot interpret an objective as figure at the same time.
- Principle of enclosure: the lines of a surface are better captured as a unit in equal circumstances.
- Principle of equality: there is a tendency to constitute groups with elements that are equal.
Application of Gestalt theory in education
The Gestalt theory is considered one of the most important contributions in the field of education through productive thinking. This position fundamentally emphasizes the way of understanding and the rules that govern the action and understanding of different meanings. It sought to demonstrate that students could learn better through rules rather than memorization. In this way, a vision of the whole is sought in order to then be able to consider its different parts.
Representatives
Among the main representatives of the theory we can mention Max Wertheimer, who was a German psychologist who carried out the first experiment of the theory. Wolfgang Köhler, was one of the main representatives and was the one who established the concept of insight learning. Kurt Koffka, German psychologist and founder of the Gestalt school of psychology. Kurt Lewin, American psychologist who conducted research on human behavior and specialized in group dynamics. Friedrich Solomon Perls, Jewish.
Examples
An example of the theory is that before we looked for a way to teach and learn first knowing the letters of the alphabet, then the syllables and finally the words and phrases. The Gestalt theory says that first, phrases must be learned, and then they must be broken down into syllables to finally discover and learn the letters that make them up.
How to cite this article?
Briceño V., Gabriela. (2019). Gestalt theory. Recovered on 23 February, 2024, de Euston96: https://www.euston96.com/en/gestalt-theory/